grep命令保留第一行(C语言实现)
Linux中的 grep 是一种强大的文本搜索工具,它能使用正则表达式搜索文本,并把匹配的行打印出来。特别是在搜索日志、配置文件、过滤时应用非常广泛。
grep 与管道配合使用时,我们想要同时输出的第一行和匹配行。第一行的描述信息有助于我们理解后面每个字段的含义。
比如我们查看和sda有关的文件系统
1
2
3
4
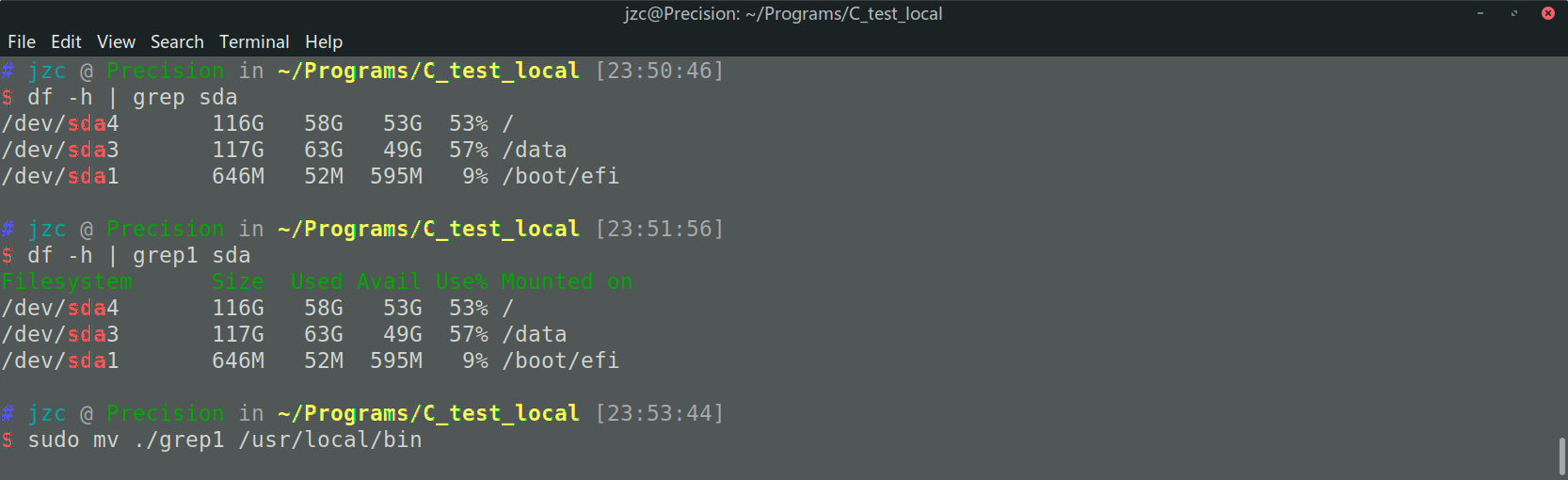
$ df -h | grep sda
/dev/sda4 116G 58G 53G 53% /
/dev/sda3 117G 63G 49G 57% /data
/dev/sda1 646M 52M 595M 9% /boot/efi
这里的116G 58G 53G 分别表示什么? 哪个才是剩余空间?
我们希望得到简单直接、一目了然的结果:
1
2
3
4
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda4 116G 58G 53G 53% /
/dev/sda3 117G 63G 49G 57% /data
/dev/sda1 646M 52M 595M 9% /boot/efi
实现方法
Stackoverflow给出的几种方案
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9969414/always-include-first-line-in-grep
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SED:
sed '1p;/pattern/!d' input.txt
AWK:
awk 'NR==1 || /pattern/' input.txt
grep1:
grep1() { awk -v pattern="${1:?pattern is empty}" 'NR==1 || $0~pattern' "${2:?filename is empty}"; }
这些方法不够好、不够方便、不够优雅。
为什么? 比如sudo netstat -nplt 标题在第二行,其余大多数命令的标题在第一行。不能简单根据行号来判断。再就是这样写比较麻烦,比 grep 差远了
于是我用C语言写了一个程序 grep1 ,它可以智能判断标题行,输出彩色标题后调用 grep 完成匹配搜索。因为是调用 grep 的,所以 grep 能用的参数这里也可以用。
效果对比
下面是源码 grep1.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int is_title(char *s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s) - 2; ++i)
{
if (s[i] == s[i+1] && s[i] == s[i+2])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
/* compose command */
char command[500] = "grep --color=always --exclude-dir={.bzr,CVS,.git,.hg,.svn} ";
char sep[] = " ";
for (int i = 1; argv[i] != NULL; ++i)
{
strcat(command, sep);
strcat(command, argv[i]);
}
/* find title line */
char buffer[500];
char flows[3000] = {0};
while (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), stdin) != NULL)
{
if (is_title(buffer))
{
/* use green color to highlight title */
printf("\033[;32m");
printf("%s", buffer);
printf("\033[0m");
break;
}
/* save read string */
strncat(flows, buffer, (size_t)(3000 - strlen(flows)));
}
fflush(stdout);
/* call grep */
FILE *fp;
int c;
char *flow_point = flows;
fp = popen(command, "w");
if (fp != NULL)
{
while ((c = *flow_point++) != 0)
putc(c, fp);
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
putc(c, fp);
putc(EOF, fp);
pclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
编译后移动到 /usr/local/bin/grep1 ,PATH环境变量一般包含 /usr/local/bin
用法示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
$ sudo netstat -nplt | grep1 3306
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1047/mysqld
$ df -h | grep1 sda
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda4 116G 58G 53G 53% /
/dev/sda3 117G 63G 49G 57% /data
/dev/sda1 646M 52M 595M 9% /boot/efi
$ ps -aux|grep1 kcp
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
jzc 2367 1.0 0.1 108680 9784 tty1 Sl+ Apr26 8:23 /home/jzc/kcptun -l :9001 -r 67.216.199.87:29900 --key very fast --crypt none --mode fast3 --sndwnd 512 --rcvwnd 512
jzc 2368 0.0 0.1 49604 15072 tty1 S+ Apr26 0:11 /usr/bin/python /home/jzc/.local/bin/sslocal -c /home/jzc/ss_kcptun.json
jzc 8864 0.0 0.0 4508 712 pts/0 S+ 00:15 0:00 grep1 kcp